

Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is characterized by a variety of common symptoms. These may include severe and continuous pain that is disproportionate to the initial injury or trauma, as well as changes in skin color and temperature in the affected area. Swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion are also common symptoms. Additionally, individuals with CRPS may experience abnormal sweating, changes in nail and hair growth patterns, and muscle weakness. It is important to note that the symptoms of CRPS can vary from person to person and may change over time.
The diagnosis of Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) can be challenging, as there is no specific test to confirm its presence. Instead, healthcare professionals rely on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and the presence of characteristic symptoms. Diagnostic criteria, such as those established by the International Association for the Study of Pain, may be used to aid in the diagnosis. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or bone scans, may also be performed to rule out other conditions and assess the extent of the disease.
Andrew is back talking about a colleague's recent case. This is a new grad, only practicing for 5 weeks or so, but kudos to his differential diagnosis skills and applying the Wells Criteria for Pulmonary Embolism. If you're not familiar with it, its something you should keep in the back of your mind, especially with post op patients, those who have been recently immobilized, or with history of Cancer or PE. Untold Physio Stories is sponsored byThe Eclectic Approach Network - Check out Dr. E's all new private, non tracking and ad free network for rehab pros! It's free to join, has chat, feed, and all the features of other social networks without the creeping tracking.Check out EDGE Mobility System's Best Sellers - Something for every PT, OT, DC, MT, ATC or Fitness Minded Individual https://edgemobilitysystem.comCurv Health - Start your own Virtual Clinic Side Hustle for FREE! Create your profile in 3 minutes, set your rates, and Curv will handle the rest! From scheduling to payments, messaging, charting, and a full exercise library that allow for patient/clinician tracking, it's never been easier! Click to join Dr. E's new Virtual Clinic Collective to help promote best online practices. Keeping it Eclectic... This article was originally posted on Modern Manual Therapy Blog

Posted by on 2023-07-26
Collagen Supplementation for Joint Pain and Arthritis: Does it Really Work?By Dr. Sean M.Wells, DPT, PT, OCS, ATC/L, CSCS, NSCA-CPT, CNPT, Cert-DNRecently I was presenting at the annual conference of Athletic Trainers' Association of Florida (ATAF) and I was overwhelmed by one consistent question: why didn't you talk about collagen supplementation? My talk was specifically on orthopedics for older adults and naturally I focused on osteoarthritis (OA) and how important exercise and diet are for that condition. I did touch on some supplementation, but I left off collagen because my last examination of this supplement, using one of my favorite websites Examine.com, yielded mediocre results. However the participants at the sports medicine conference piqued my interest and convinced me that perhaps I had missed something -- almost every single one of these participants had some form of joint pain or stiffness and felt significantly better after taking collagen daily. So, back to the literature, and asking some of my clients, I went!What is Collagen?Collagen is a protein found in the body that provides structure and support to various tissues, including joints, bones, tendons, and ligaments. It may play a role in maintaining joint health and may have potential benefits for individuals with joint pain. A few small-scale studies have shown positive results in reducing joint pain and improving joint function when individuals with osteoarthritis took collagen supplements. These studies often used specific collagen formulations, such as collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen, which are broken down into smaller peptides for better absorption by the body. However, it's important to note that the findings of these studies are not yet conclusive, and more robust research is necessary.The ResearchIt's worth mentioning that joint pain can have various causes, and collagen supplementation may not be effective for everyone. Factors like age, underlying health conditions, overall diet, and lifestyle habits can also influence joint health. For instance, a meta-analysis on collagen supplementation for OA showed improvements in the WOMAC, a functional score for knee arthritis, but it didn't yield significant results for knee pain. Meanwhile, another review article looking at collagen supplementation for joint pain, muscle protein synthesis, and body composition found that collagen did significantly reduce joint pain (it had effect on the other metrics). Here's a nice table listed in the article:The joint pain included in the review included knee pain and Achilles tendinopathy, all predominately in an athletic population. Another glaring observation is several of these studies included physical therapy and exercise prescriptions with the supplementation (Yay! Nutrition and Physical Therapy), which can also alter the results and effects of collagen as well. It's important to see the doses varied in the studies from 5, 10, to 40 grams per day; moreover, the collagen can come in varying form from peptides, hydrolyzed proteins, to denatured collagen. Having such variability in the type of collagen also likely explains the variability in responses and data.DosingSo, roughly how much and what type of collagen should a client take? Well, many studies have used dosages ranging from 8 to 12 grams of collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen per day for joint-related benefits. Research suggests that type II collagen supplementation may help reduce joint pain and improve joint function in individuals with arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis. It is believed to work by helping to restore and support cartilage health, potentially reducing inflammation and promoting joint mobility. It's important to note that collagen supplements are available in various forms, such as powders, capsules, and liquids, and their concentration of collagen can vary. Therefore, it's crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.It's also worth mentioning that collagen supplements are often combined with other ingredients, such as vitamins, minerals, or herbal extracts, which may influence their effectiveness. If you decide to try collagen supplementation for joint pain, it's a good idea to choose a reputable brand and look for products that have been tested for quality and safety. I suggest using Labdoor.com to help you or your client find a high-quality collagen supplement, if and when appropriate.SummaryIn the end, perhaps the participants at the ATAF conference were right -- there is something to say about collagen and joint pain. Not every study is exact and more research needs to be done on what dose, what age, what condition, and what exercises should be done with the collagen -- but that's why we practice physical therapy! Love to hear your thoughts and maybe some of your clients' responses to collagen. If you like what you see here then know there is more in our 3 board-approved continuing education courses on Nutrition specific for Physical Therapists. Enroll today in our new bundled course offering and save 20%, a value of $60! Earn CEUs in most states for PTs! Want to learn in person? Attend a #manualtherapyparty! Check out our course calendar below! Learn more online - new online discussion group included! Want an approach that enhances your existing evaluation and treatment? No commercial model gives you THE answer. You need an approach that blends the modern with the old school. NEW - Online Discussion Group Live cases webinars lecture Live Q&A over 600 videos - hundreds of techniques and more! Check out MMT Insiders Keeping it Eclectic... This article was originally posted on Modern Manual Therapy Blog
![[RESEARCH] Collagen Supplementation for Joint Pain and Arthritis: Does it Really Work?](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgNRlO03OFOpdytY9td2mMDwpqFwMqHyUpqlQukvulwJkAaq6-RVGwr1keXUlLXifkdyTTWv66um_-YJFeEDqBBymiw14ZWWFPPem3W4DZrzncQYGpZkWWsxSuZhi6eaJN19b1AkC6SMBeCDeEBF1DYueqVTCUD80jq5SJkKqc2Tokr3FWbElnPb8LbnhP0/s16000/knee%20oa.jpg)
Posted by on 2023-07-24
In this episode, Erson goes over a tough case of constant and flared up cervical pain with radiating complaints. What do you think of his solution? Have you ever had a similar case that responded to sustained holds better than repeated loading or traditional techniques? Untold Physio Stories is sponsored byThe Eclectic Approach Network - Check out Dr. E's all new private, non tracking and ad free network for rehab pros! It's free to join, has chat, feed, and all the features of other social networks without the creeping tracking.Check out EDGE Mobility System's Best Sellers - Something for every PT, OT, DC, MT, ATC or Fitness Minded Individual https://edgemobilitysystem.comCurv Health - Start your own Virtual Clinic Side Hustle for FREE! Create your profile in 3 minutes, set your rates, and Curv will handle the rest! From scheduling to payments, messaging, charting, and a full exercise library that allow for patient/clinician tracking, it's never been easier! Click to join Dr. E's new Virtual Clinic Collective to help promote best online practices. Keeping it Eclectic... This article was originally posted on Modern Manual Therapy Blog

Posted by on 2023-07-17
Erson tells a story of getting back to rock climbing after a 20 year break. After a finger injury that wasn't healing, he got some totally unexpected great advice from another climber. What do you think of the solution and has anything similar ever happened to you? Untold Physio Stories is sponsored byThe Eclectic Approach Network - Check out Dr. E's all new private, non tracking and ad free network for rehab pros! It's free to join, has chat, feed, and all the features of other social networks without the creeping tracking.Check out EDGE Mobility System's Best Sellers - Something for every PT, OT, DC, MT, ATC or Fitness Minded Individual https://edgemobilitysystem.comCurv Health - Start your own Virtual Clinic Side Hustle for FREE! Create your profile in 3 minutes, set your rates, and Curv will handle the rest! From scheduling to payments, messaging, charting, and a full exercise library that allow for patient/clinician tracking, it's never been easier! Click to join Dr. E's new Virtual Clinic Collective to help promote best online practices. Keeping it Eclectic... This article was originally posted on Modern Manual Therapy Blog

Posted by on 2023-07-06
There are several treatment options available for individuals with Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). These may include a combination of medication, physical therapy, and psychological interventions. Medications commonly used to manage CRPS include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and certain antidepressants or anticonvulsants. Physical therapy, including exercises to improve range of motion and strength, as well as techniques such as mirror therapy or desensitization exercises, can also be beneficial. Psychological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or relaxation techniques, may help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological impact of CRPS.
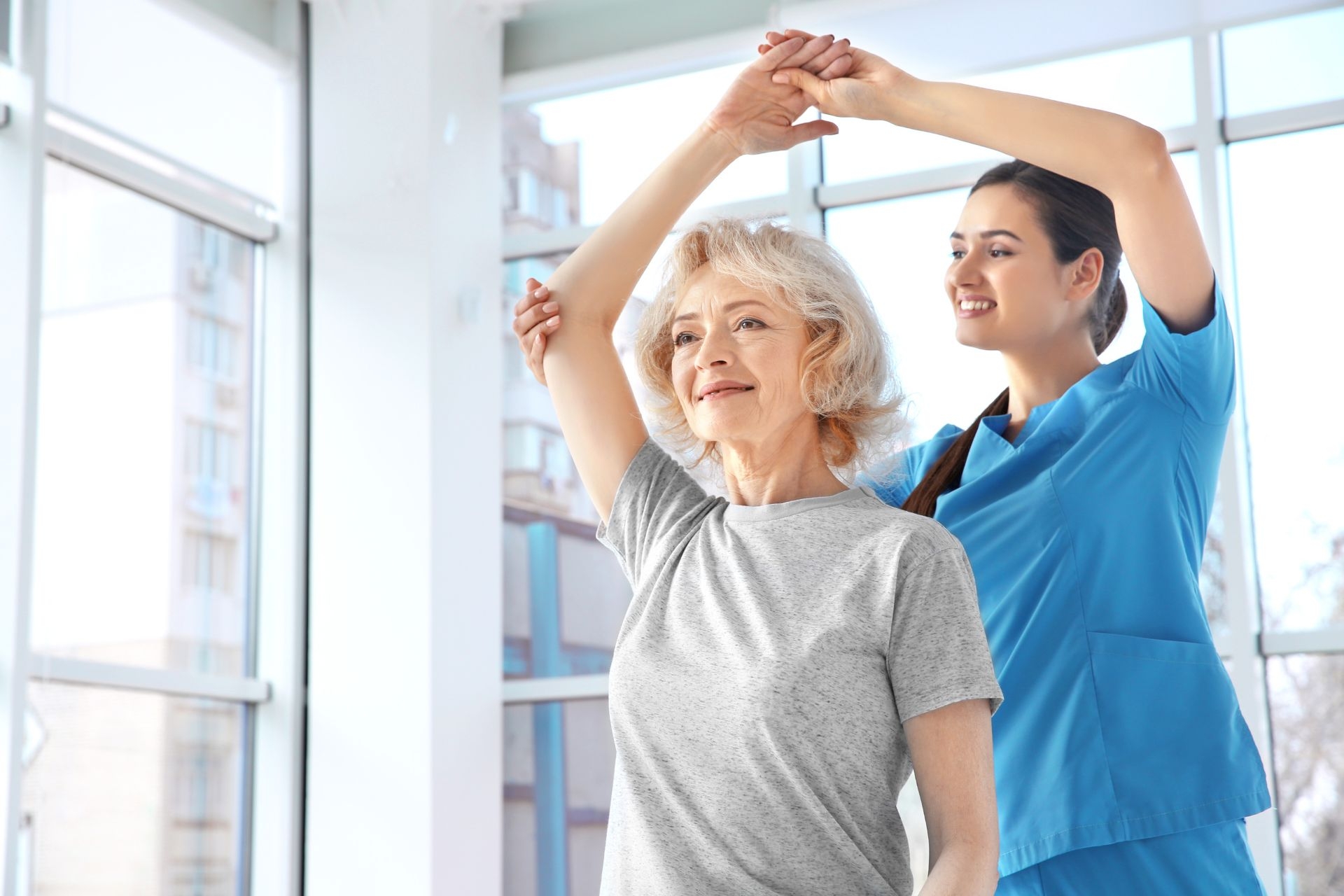

Physical therapy can play a crucial role in managing Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). It can help improve range of motion, strength, and function in the affected limb or body part. Physical therapists may use a variety of techniques, such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities like heat or cold therapy, to reduce pain and improve function. Additionally, physical therapists can educate individuals about pain management strategies and provide support throughout the rehabilitation process. It is important to work with a skilled physical therapist who has experience in treating CRPS to ensure the best possible outcomes.
While there are no medications specifically approved for the management of Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), certain medications can be used to help alleviate symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can also be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling. In some cases, antidepressants or anticonvulsants may be used to help manage pain and improve mood. However, it is important to note that medication management should be individualized and tailored to each person's specific needs.

Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) can lead to a range of potential complications. These may include muscle atrophy, joint stiffness, and contractures, which can result in decreased range of motion and functional limitations. Individuals with CRPS may also experience psychological and emotional complications, such as depression, anxiety, and difficulty coping with chronic pain. Additionally, CRPS can have a significant impact on quality of life, affecting daily activities, work, and relationships. It is important for individuals with CRPS to receive comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Currently, there is no known cure for Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). However, with appropriate treatment and management, many individuals with CRPS are able to achieve significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life. The goal of treatment is to reduce pain, improve function, and enhance overall well-being. This may involve a multidisciplinary approach, including medication management, physical therapy, psychological interventions, and other complementary therapies. It is important for individuals with CRPS to work closely with a healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Therapists modify exercise programs for individuals with multiple sclerosis by tailoring the exercises to address the specific needs and limitations of each individual. They may incorporate a variety of exercises that focus on improving balance, coordination, strength, and flexibility. These exercises may include low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling, as well as exercises that target specific muscle groups affected by multiple sclerosis. Therapists may also incorporate assistive devices or adaptive equipment to ensure safety and maximize the benefits of the exercises. Additionally, therapists may adjust the intensity and duration of the exercises based on the individual's abilities and energy levels. Regular monitoring and reassessment of the exercise program are essential to ensure its effectiveness and make any necessary modifications.
Aquatic exercise programs have shown promising results in improving motor function in children with cerebral palsy. These programs involve engaging in physical activities in water, which provide a supportive and low-impact environment for children with motor impairments. The buoyancy of water reduces the effects of gravity, allowing children to move more freely and with less effort. Additionally, the resistance provided by water helps to strengthen muscles and improve coordination. Aquatic exercise programs often incorporate various exercises and activities that target specific motor skills, such as balance, coordination, and strength. Research studies have demonstrated that these programs can lead to significant improvements in motor function, including increased muscle strength, improved balance and coordination, and enhanced overall motor performance. Furthermore, the enjoyable and stimulating nature of aquatic exercise can also contribute to increased motivation and engagement in physical activity, which further supports the development of motor skills in children with cerebral palsy.
Hydro-massage therapy has been shown to effectively alleviate muscle soreness and improve recovery post-exercise. This type of therapy utilizes water pressure and massage techniques to target specific muscle groups, promoting increased blood flow and circulation. The hydro-massage therapy also helps to reduce inflammation and swelling, which are common after intense physical activity. Additionally, the combination of water and massage provides a soothing and relaxing effect, helping to relieve muscle tension and promote overall relaxation. By incorporating hydro-massage therapy into a post-exercise routine, individuals can experience faster recovery times and reduced muscle soreness, allowing them to return to their training or physical activities more quickly.
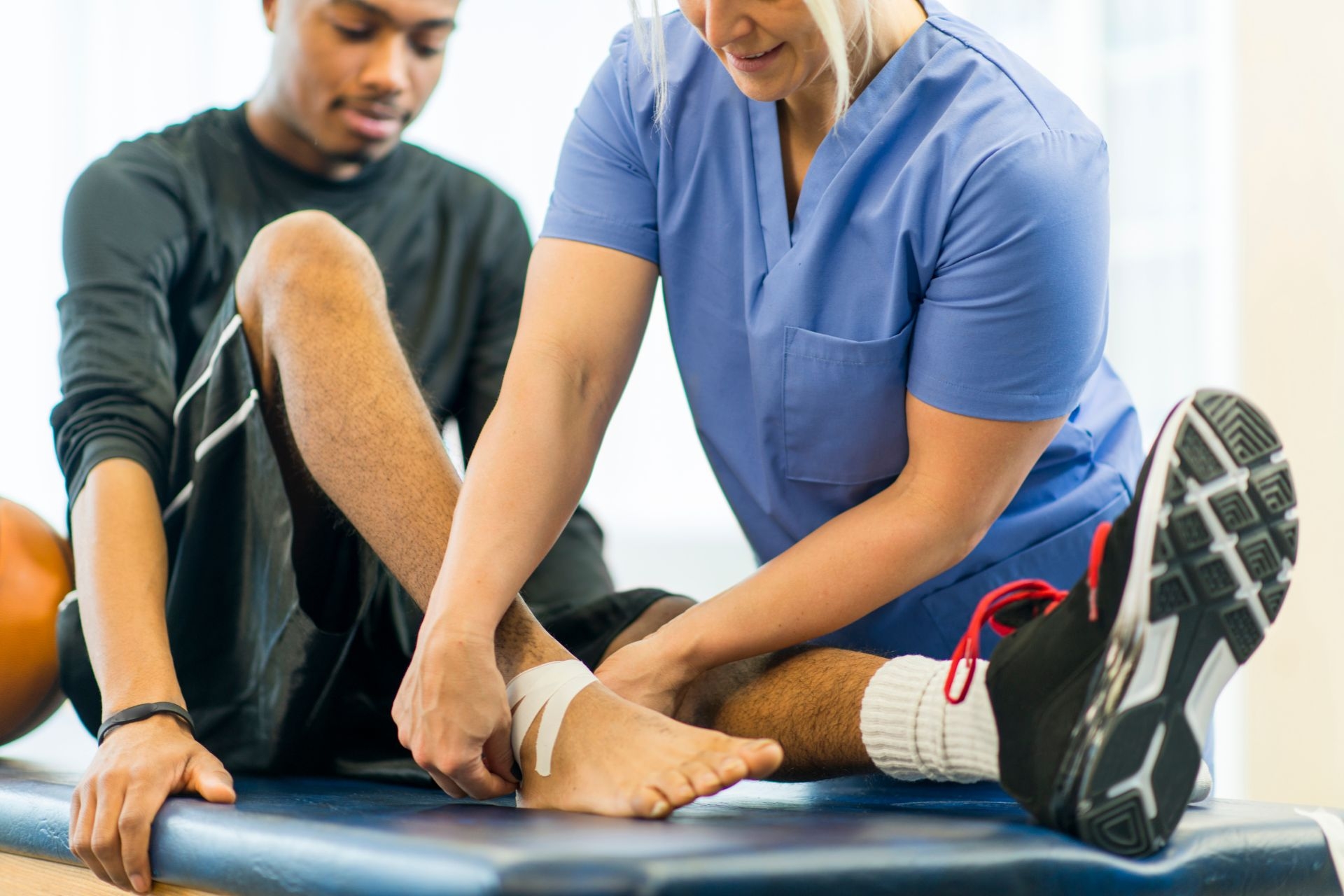
Taping techniques can be beneficial in the management of Achilles tendinopathy when certain indications are present. These indications include pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon, limited range of motion in the ankle joint, and instability in the lower leg. Taping can help provide support and stability to the affected area, reducing stress on the tendon and allowing for proper healing. Additionally, taping can help improve proprioception and neuromuscular control, which can aid in the rehabilitation process. By using taping techniques, healthcare professionals can effectively manage Achilles tendinopathy and promote optimal recovery for their patients.
High-velocity thrust manipulation in spinal manipulation therapy carries potential risks that should be carefully considered. One of the main concerns is the risk of injury to the spinal cord or nerves, which can result in neurological complications such as paralysis or sensory deficits. Additionally, there is a risk of fractures or dislocations of the vertebrae, especially in individuals with pre-existing spinal conditions or osteoporosis. Other potential risks include muscle strains, ligament sprains, and soft tissue injuries. It is important for practitioners to have a thorough understanding of the patient's medical history and to perform a comprehensive examination before administering high-velocity thrust manipulation to minimize these risks.
The Feldenkrais Method is a somatic educational approach that aims to improve movement efficiency and coordination through increased body awareness and exploration of movement patterns. By engaging in gentle, slow, and mindful movements, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of their own movement habits and limitations. This increased self-awareness allows for the identification and release of unnecessary tension and effort, leading to more efficient movement patterns. Additionally, the Feldenkrais Method emphasizes the integration of the whole body, promoting coordination and fluidity in movement. Through the exploration of different movement possibilities and variations, individuals can expand their movement repertoire and enhance their overall coordination. By addressing the underlying neuromuscular patterns that contribute to inefficient movement, the Feldenkrais Method offers a holistic approach to improving movement efficiency and coordination.